Integrate with PostgreSQL
This authorizer implements authorization checks through matching publish/subscription requests against lists of rules stored in the PostgreSQL database.
Prerequisite
Knowledge about basic EMQX authorization concepts
Data Schema and Query Statement
PostgreSQL authorizer supports almost any storage schema. It is up to the user to decide how to store acl rules and access them: using one or multiple tables, views, etc.
Users need to provide a query statement template and ensure the following fields are included:
permissionvalue specifies the applied action if the rule matches. Should be one ofdenyorallow.actionvalue specifies the request for which the rule is relevant. Should be one ofpublish,subscribe, orall.topicvalue specifies the topic filter for topics relevant to the rule. Should be a string that supports wildcards and topic placeholders.qos(Optional) value specifies the QoS levels that the rule applies to. Value options are0,1,2. It can also be a string separated by,to specify multiple QoS levels, e.g.0,1. The default is all QoS levels.retain(Optional) value specifies whether the current rule supports retained messages. Value options are0and1. The default is to allow retained messages.
Example table structure for storing credentials:
CREATE TYPE ACTION AS ENUM('publish','subscribe','all');
CREATE TYPE PERMISSION AS ENUM('allow','deny');
CREATE TABLE mqtt_acl (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
ipaddress CHARACTER VARYING(60) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
username CHARACTER VARYING(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
clientid CHARACTER VARYING(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
action ACTION,
permission PERMISSION,
topic CHARACTER VARYING(255) NOT NULL,
qos tinyint,
retain tinyint
);
CREATE INDEX mqtt_acl_username_idx ON mqtt_acl(username);In this table, MQTT users are identified by username.
For example, if you want to add an authorization rule for a user user123 who is allowed to publish topics data/user123/#, the query statement should be:
postgres=# INSERT INTO mqtt_acl(username, permission, action, topic, ipaddress) VALUES ('user123', 'allow', 'publish', 'data/user123/#', '127.0.0.1');
INSERT 0 1The corresponding config parameters are:
query = "SELECT permission, action, topic, ipaddress, qos, retain FROM mqtt_acl WHERE username = ${username} and ipaddress = ${peerhost}"Configure with Dashboard
You can use EMQX Dashboard to configure how to use PostgreSQL for user authorization.
On EMQX Dashboard, click Access Control -> Authorization on the left navigation tree to enter the Authorization page.
Click Create at the top right corner, then click to select PostgreSQL as Backend. Click Next. The Configuration tab is shown as below.
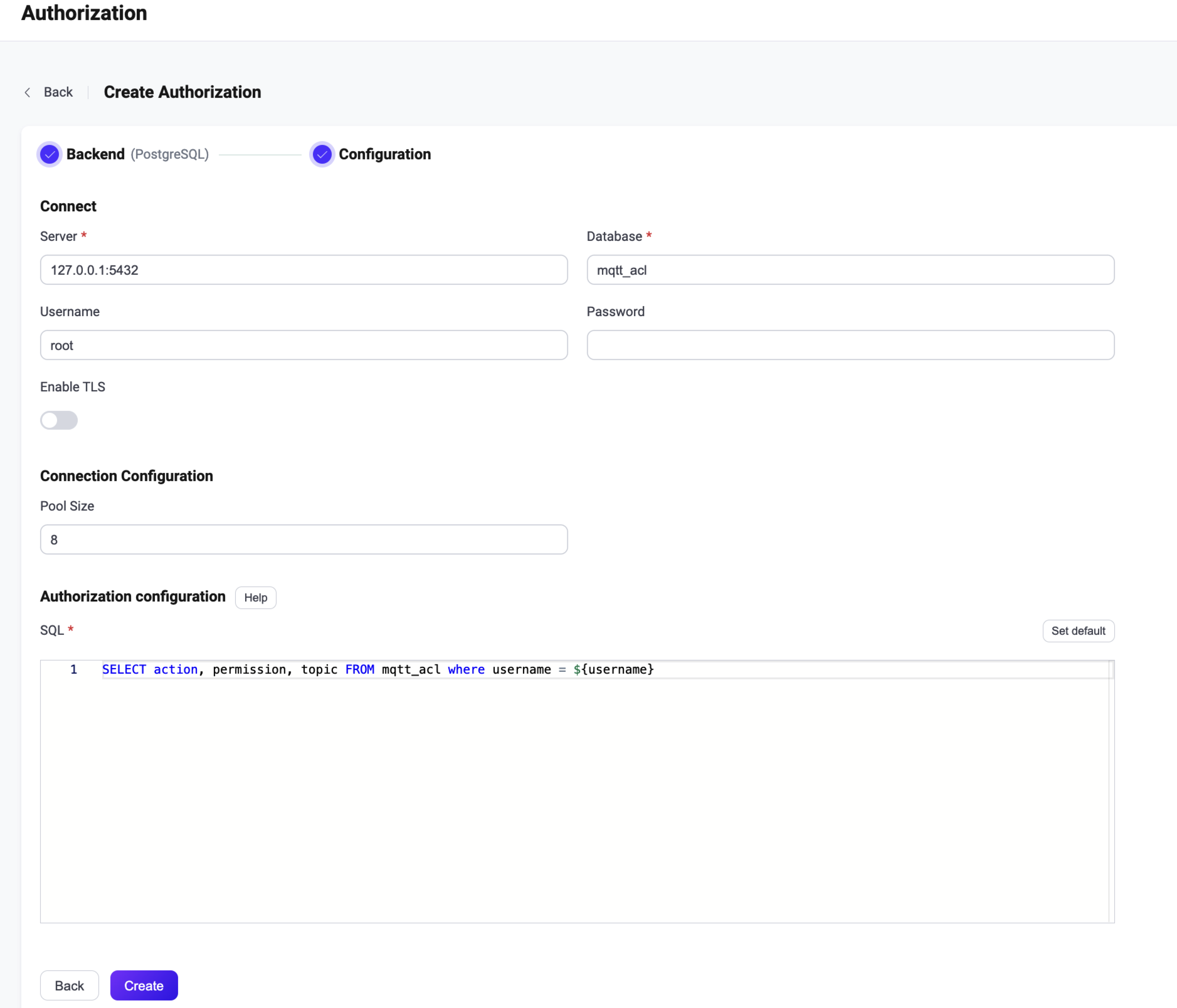
Follow the instructions below to do the configuration.
Connect: Fill in the information needed to connect PostgreSQL.
- Server: Specify the server address that EMQX is to connect (
host:port). - Database: PostgreSQL database name.
- Username (optional): Specify user name.
- Password (optional): Specify user password.
TLS Configuration: Turn on the toggle switch if you want to enable TLS.
Connection Configuration: Set the concurrent connections and waiting time before a connection is timed out.
- Pool size (optional): Input an integer value to define the number of concurrent connections from an EMQX node to PostgreSQL. Default: 8.
Authorization configuration: Fill in the authorization-related settings:
- SQL: Fill in the query statement according to the data schema. For more information, see Data Schema and Query Statement.
- Server: Specify the server address that EMQX is to connect (
Click Create to finish the settings.
Configure with Configuration Items
You can configure the EMQX PostgresSQL authorizer with EMQX configuration items.
The PostgreSQL authorizer is identified by type postgresql.
Sample configuration:
{
type = postgresql
enable = true
database = "mqtt"
username = "postgres"
password = "public"
server = "127.0.0.1:5432"
query = "SELECT permission, action, topic FROM mqtt_acl WHERE username = ${username}"
}