Performance Test with eMQTT-Bench
After you deploy the EMQX either in a single mode or in an EMQX cluster, you can test the performance of your deployment to know the system capability. This section introduces how to install and use the eMQTT-Bench to do the performance test. The eMQTT-Bench is a concise and powerful MQTT protocol benchmark tool written with Erlang. If you need testing services with large-scale scenarios and in-depth customization, the test service XMeter is recommended.
Install eMQTT-Bench
There are three options for installing the eMQTT-Bench:
- Run the docker image
- Download and install the binary package
- Build from the source code
Docker Image
You can install the benchmark tool by running the emqtt-bench docker image pushed to hub.docker.com. The :latest tag is updated with each new version:
docker run -it emqx/emqtt-bench:latest
Usage: emqtt_bench pub | sub | conn [--help]Note that the docker image name uses hyphen '-', while the binary script name uses with underscore '_'.
Binary Package
You can download the released binary packages and install the emqtt-bench on the following platforms:
- Amazon Linux 2
- Amazon Linux 2023
- CentOS 7
- Rocky Linux 8
- Rocky Linux 9
- Debian 9
- Debian 10
- Debian 11
- Debian 12
- Ubuntu 16.04
- Ubuntu 18.04
- Ubuntu 20.04
- Ubuntu 22.04
- MacOS 11 (Intel)
- MacOS 12 (Intel)
- MacOS 12 (Apple Silicon)
For detailed information on each release, see Releases.
For example, here is how to install emqtt-bench on Ubuntu 20.04:
mkdir emqtt-bench && cd emqtt-bench
wget https://github.com/emqx/emqtt-bench/releases/download/0.4.12/emqtt-bench-0.4.12-ubuntu20.04-amd64.tar.gz
tar xfz emqtt-bench-0.4.12-ubuntu20.04-amd64.tar.gz
rm emqtt-bench-0.4.12-ubuntu20.04-amd64.tar.gz
./emqtt_bench
Usage: emqtt_bench pub | sub | conn [--help]Build from Source
The eMQTT-Bench is written in Erlang and requires Erlang/OTP 22.3 and above version to build it. The installation process of Erlang/OTP is skipped. For details, please refer to the online installation tutorials.
After the Erlang environment is installed, download the latest code of emqtt-bench and compile it:
git clone https://github.com/emqx/emqtt-bench
cd emqtt-bench
makeAfter the compilation, an executable script named emqtt_bench will be generated in the current directory. Execute the following command to confirm that it can be used normally:
./emqtt_bench
Usage: emqtt_bench pub | sub | conn [--help]The output of the above content proves that emqtt-bench has been correctly installed on the host.
Use eMQTT-Bench
There are three subcommands of emqtt_bench:
pub: Create a large number of clients to perform the operation of publishing messages.sub: Create a large number of clients to subscribe to topics and receive messages.conn: Create a large number of connections.
Publish
When executing ./emqtt_bench pub --help, you get the available parameter output.
| Parameter | Abbreviation | Optional Value | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| --host | -h | - | localhost | Address of the MQTT server to connect |
| --port | -p | - | 1883 | MQTT service port |
| --version | -V | 3 4 5 | 5 | MQTT protocol version used |
| --count | -c | - | 200 | Total number of clients |
| --startnumber | -n | - | 0 | Start number of clients |
| --interval | -i | - | 10 | Interval to create a client; unit: ms |
| --interval_of_msg | -I | - | 1000 | Interval to publish a message |
| --username | -u | - | None; optional | Client username |
| --password | -P | - | None; optional | Client password |
| --topic | -t | - | None; required | Published topics; support placeholders:%c: ClientId%u: Username%i: Client's sequence number |
| --size | -s | - | 256 | Message Payload size; unit: bytes |
| --qos | -q | - | 0 | QoS level |
| --retain | -r | true false | false | Whether the message sets the Retain flag |
| --keepalive | -k | - | 300 | Client keepalive time |
| --clean | -C | true false | true | Whether to establish a connection by cleaning the session |
| --ssl | -S | true false | false | Whether to enable SSL |
| --certfile | - | - | None | Client SSL certificate |
| --keyfile | - | - | None | Client SSL key file |
| --ws | - | true false | false | Whether to establish a connection via WebSocket |
| --ifaddr | - | - | None | Specifies the local network card used by the client connection |
For example, you can start 10 connections and send 100 Qos0 messages to the topic t every second, where the size of each message payload is 16 bytes:
./emqtt_bench pub -t t -h emqx-server -s 16 -q 0 -c 10 -I 10Subscribe
Execute ./emqtt_bench sub --help to get all available parameters of this subcommand. Their explanations have been included in the table above and are omitted here.
For example, you can start 500 connections, and each subscribes to the t topic with Qos0:
./emqtt_bench sub -t t -h emqx-server -c 500Connect
Execute ./emqtt_bench conn --help to get all available parameters of this subcommand. Their explanations have been included in the table above and are omitted here.
For example, you can start 1000 connections:
./emqtt_bench conn -h emqx-server -c 1000SSL Connection
emqtt-bench supports establishing a secure SSL connection and performing tests.
One-way certificate:
./emqtt_bench sub -c 100 -i 10 -t bench/%i -p 8883 -S
./emqtt_bench pub -c 100 -I 10 -t bench/%i -p 8883 -s 256 -STwo-way certificate:
./emqtt_bench sub -c 100 -i 10 -t bench/%i -p 8883 --certfile path/to/client-cert.pem --keyfile path/to/client-key.pem
./emqtt_bench pub -c 100 -i 10 -t bench/%i -s 256 -p 8883 --certfile path/to/client-cert.pem --keyfile path/to/client-key.pemPerform Stress Test
This section describes how to perform stress tests on in 2 typical scenarios: connection and throughput.
Typical Stress Test Scenarios
Verify the use of the tool in 2 most typical scenarios:
- Connections: Use
emqtt-benchto create millions of connections to EMQX. - Throughput: Use
emqtt-benchto create100k/s Qos 0message throughput in EMQX.
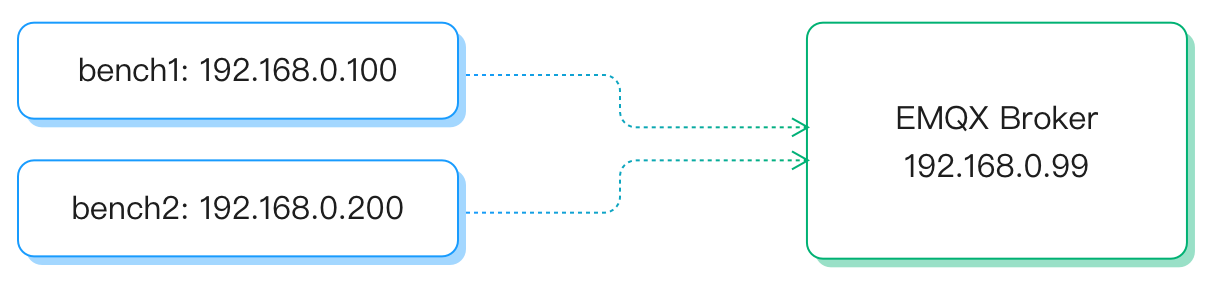
Device and Deployment Topology
A total of three 8C16G servers need to be prepared, one for EMQX and two for client presses:
System:
CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908 (Core)CPU:
Intel Xeon Processor (Skylake)Main frequency:2693.670 MHZServer:
emqx-centos7-v4.0.2.zipPress:
emqtt-bench v0.3.1, each press is configured with 10 network cards, which are used to establish a large number of MQTT client connections in the connection test
The topology structure is as follows:
Tuning
Both the client's press and the server's machine need to perform system parameter tuning, refer to Tuning guide.
Connection Test
After performing system tuning, start EMQX, then start 50 thousand connections on each network card on bench1, which is a total of 50w connections:
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.100
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.101
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.102
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.103
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.104
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.105
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.106
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.107
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.108
./emqtt_bench -h 192.168.0.99 -c 50000 --ifaddr 192.168.0.109Perform the same operation on bench2.
After all the connections are established, execute ./bin/emqx ctl listeners and you will find the following information about the number of connections in EMQX:
listener on mqtt:tcp:0.0.0.0:1883
acceptors : 8
max_conns : 1024000
current_conn : 1000000
shutdown_count : []Throughput Test
Similarly, first start EMQX, then start 500 subscription clients in bench1:
./emqtt_bench sub -t t -h 192.168.0.99 -c 500Then start 20 publishers on bench2 and publish 10 messages per second:
./emqtt_bench pub -t t -h 192.168.0.99 -c 20 -I 100Go back to the subscribing client on bench1, you can see the current rate of receiving messages:
recv(28006): total=2102563, rate=99725(msg/sec)