Cluster
Besides working with a single EMQX node, EMQX natively supports a distributed cluster architecture, which can handle a large number of clients and messages while ensuring high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability. With the EMQX cluster, you can enjoy the benefits of fault tolerance and high availability by allowing the cluster to continue operating even if one or more nodes fail.
This chapter introduces the benefits of clustering, the new Mria and RLOG architecture, how to create a cluster manually or automatically, how to implement load balancing, and how to ensure communication security within a cluster.
Reasons for Clustering
EMQX cluster is recommended for larger or mission-critical applications and can bring the users the following benefits.
- Scalability: EMQX can be easily scaled horizontally by adding more nodes to the cluster, allowing it to handle an increasing number of MQTT messages and clients.
- High Availability: Running in a cluster provides high availability, as the cluster can continue to function even if one or more nodes fail. EMQX uses a distributed architecture that ensures no single point of failure.
- Load Balancing: EMQX nodes in the cluster can be configured to distribute the load of handling MQTT messages, which helps to avoid overload of a single node and allows for better use of available resources.
- Centralized Management: EMQX can be managed centrally, as all nodes in the cluster can be monitored and controlled from a single management console. This makes it easy to manage a large number of devices and messages.
- Data Consistency and Security: The cluster replicates data across all nodes in the cluster, which helps to ensure data consistency and security.
How Clustering in EMQX Works
The basic function of a distributed EMQX cluster is to forward and publish messages to different subscribers. In previous versions, EMQX utilizes Erlang/OTP's built-in database, Mnesia, to store MQTT session states. The database replication channel is powered by the "Erlang distribution" protocol, enabling each node to function as both a client and server. The default listening port number for this protocol is 4370.
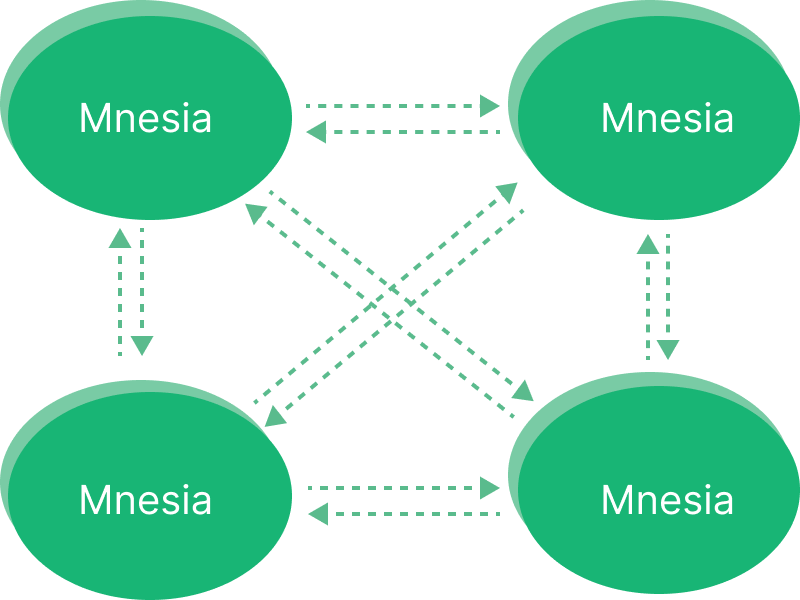
However, the full mesh topology imposes a practical limit on the cluster size. For EMQX versions prior to 5, it is recommended to keep the cluster size under 5 nodes. Beyond this, vertical scaling, which involves using more powerful machines, is a preferable option to maintain the cluster's performance and stability. In our benchmark environment, we managed to reach ten million concurrent connections with EMQX Enterprise 4.3.
To provide our customers with a better cluster salability performance, EMQX 5.0 adopts a new Mria cluster architecture. With this Mria architecture, one EMQX cluster can support up to 100 million concurrent MQTT connections.
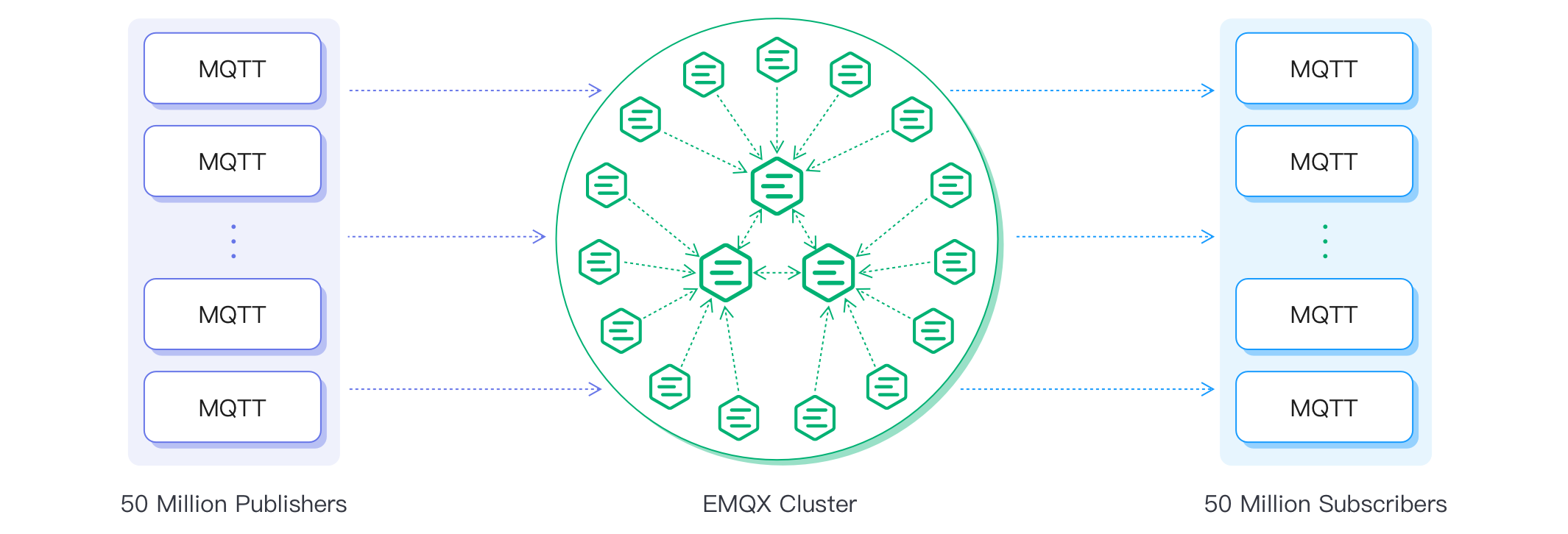
To better understand how clustering in EMQX works, you can continue to read the EMQX clustering.
Key Features
EMQX adds an abstraction layer with the Ekka library on top of distributed Erlang, enabling features like auto discovery of EMQX nodes, auto cluster, network partition, autoheal, and autoclean.
Node Discovery and Auto Clustering
EMQX supports several node discovery strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
manual | Manually create a cluster with commands |
static | Autocluster through static node list |
DNS | Autocluster through DNS A and SRV records |
etcd | Autocluster through etcd |
k8s | Autocluster provided by Kubernetes |
Network Partition Autoheal
Network partition autoheal is a feature of EMQX that allows the broker to recover automatically from network partitions without requiring any manual intervention, suitable for mission-critical applications where downtime is not acceptable.
The network partition autoheal (cluster.autoheal) feature is enabled by default. With this feature, EMQX will continuously monitor the connectivity between nodes in the cluster.
cluster.autoheal = trueIf a network partition is detected, EMQX will isolate the affected nodes and continue to operate with the remaining nodes. Once the network partition is resolved, the broker will automatically re-integrate the isolated nodes into the cluster.
Cluster Node Autoclean
Cluster node autoclean feature will automatically remove the disconnected nodes from the cluster after the configured time interval. This feature helps to ensure that the cluster is running efficiently and prevent performance degradation over time.
This feature is enabled by default, you can customize the waiting period before removing the disconnected nodes. Default: 24h
cluster.autoclean = 24hSession Across Nodes
The session across nodes feature ensures that the client sessions will not be lost even during the client's disconnection.
To use this feature:
- for MQTT 3.x clients, set
clean_starttofalse - for MQTT 5.0 clients, set
clean_starttofalseand setsession_expiry_intervalto be greater than 0.
Then EMQX will keep the previous session data associated with the Client ID when the client disconnects. If this client reconnects, EMQX will resume the previous sessions, deliver any messages that were queued during the client's disconnection, and maintain the client's subscriptions.
Network and Hardware Specifications
Below are the network requirements and hardware specifications recommend to run EMQX clusters.
Network
Network latency: < 10 ms. The cluster will not be available if the latency is higher than 100 ms.
The core nodes should be under the same private network. In Mria+RLOG mode, it is also recommended to deploy the replicant nodes in the same private network.
CPU and Memory
You can use the Server Estimate to calculate the CPU and memory resources needed under various connections and Pub&Sub TPS. It is recommended to configure a higher memory of the Core nodes.