Multi-Protocol Gateway
EMQX Multi-Protocol Gateway enables handling all non-MQTT protocol connections, authentication, and message sending and receiving. It provides a unified conceptual model for various protocols.
Before EMQX 5.0, non-MQTT protocol access was implemented by separate protocol plugins. These plugins had different design and implementation differences, making it challenging to use them.
Starting from 5.0, EMQX offers the Multi-Protocol Gateway defines a unified conceptual and operational model to make it easier to use.
The Multi-Protocol Gateway supports protocols such as MQTT-SN, STOMP, CoAP, LwM2M, etc. It can be enabled and configured directly in the Dashboard or managed using the HTTP API or emqx.conf. On how to enable these gateways and how to customize the settings to better suit your business needs, you can click the link below for details.
How the Multi-Protocol Gateway Works
EMQX Multi-Protocol Gateway defines a unified conceptual and operational model for several key components, including listeners, connections/sessions, publish/subscribe, authentication, and authorization.
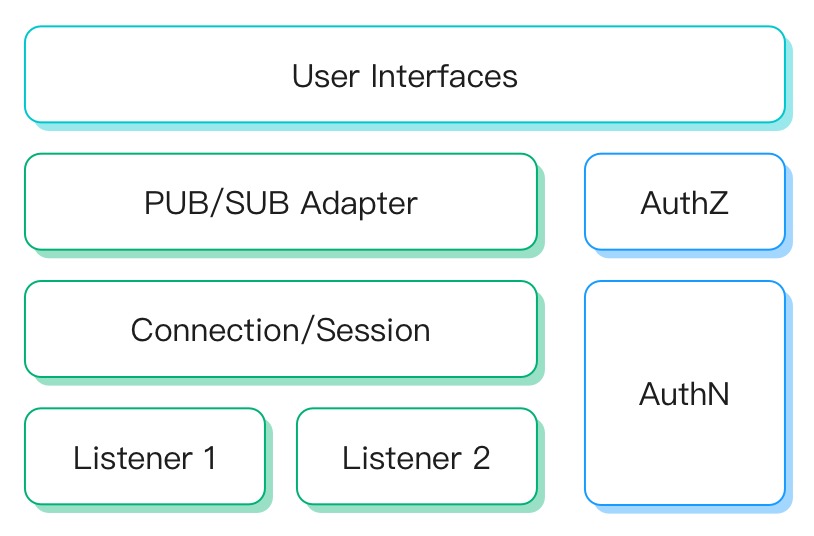
Here's a brief overview of each component:
Listener: Support listener types: TCP, SSL, UDP, DTLS. Each gateway can create multiple listeners.
Connection/Session: Gateway creates a session for each accepted client connection, which manages the subscription list, deliver/receive queue, and retransmission logic of client messages.
Publish/Subscribe: Each type of gateway defines how to adapt to the MQTT protocol's PUB/SUB message model. Non-PUB/SUB protocols require configuring message topics and payloads, and each type of gateway may use a different message format.
Authentication: Each gateway can be configured with authenticators to use the client information for login authorization.
Key Features
Listener
Each gateway can have multiple listeners enabled, and different protocol gateways support the following listener types:
| TCP | UDP | SSL | DTLS | Websocket | Websocket over TLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT-SN | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| STOMP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| CoAP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| LwM2M | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| ExProto | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||
| OCPP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| GB/T 32960 | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ||||
| JT/T 808 | ✔︎ | ✔︎ |
Message Format
To ensure compatibility with the PUB/SUB messaging model, each gateway type must adapt to the presence or absence of a PUB/SUB concept in its underlying protocol.
For protocols with a PUB/SUB concept, like MQTT-SN and Stomp, compatibility is achieved by using the client-sent topic and payload, and no message format conversion is needed.
For protocols without a PUB/SUB concept, such as CoAP and LwM2M, there are no definitions for topics, publishing, or subscribing. Here, the gateway must design the message content format, with each type potentially using a distinct format.
- CoAP: The CoAP gateway uses the URI path and methods defined in the Publish-Subscribe Broker for the CoAP standard. For details, see Message Publish, Topic Subscribe, Topic Unsubscribe.
- LwM2M: The messaging model of LwM2M protocol is based on Resources Model and Operations. This is completely different from the Publish/Subscribe model of the MQTT protocol. For details, see LwM2M Gateway - Message Format.
Authentications
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a client attempting to connect to a system. Starting from version 5.0, the gateway supports authenticators for login authorization.
Different gateways may support different types of authenticators, but all gateways support HTTP-based authentication. HTTP-based authentication. See the table below for the authentication types supported:
| HTTP Server | Built-in Database | MySQL | MongoDB | PostgreSQL | Redis | JWT | LDAP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT-SN | ✔︎ | |||||||
| STOMP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ |
| CoAP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ |
| LwM2M | ✔︎ | |||||||
| Exproto | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ |
| OCPP | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ | ✔︎ |
| GB/T 32960 | ✔︎ | |||||||
| JT/T 808 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Note: Any client can log in if no authenticator is configured.
How Authentication Works on the Gateway
The EMQX Multi-Protocol Gateway is responsible for authenticating clients that connect to it. This is accomplished through the creation of a ClientInfo for each connection.
The ClientInfo includes generic fields such as Username and Password, which are commonly used for authentication purposes. Additionally, each gateway has its own specific client information fields, such as Endpoint Name for LwM2M, which may also be used for authentication.
When an authenticator is configured, the gateway compares the client's Username and Password fields with those stored in its database. If they match, the client is authenticated and granted access to the gateway.
TIP
Client ID for different gateways can be duplicated, but when a duplicated Client ID logs in to a gateway, it will terminate the existing session associated with that Client ID.
Integration with External Systems
For better integration with external systems, the gateway also supports hooks defined in the EMQX.
Due to the heterogeneity of semantics between gateways, only some of the core hooks are available.
Client connection-related hooks with the following supportability:
For improved interoperability with external systems, the gateway is designed to support hooks as defined in EMQX.
However, due to the differences in semantics among various gateways, only a subset of the core hooks can be utilized, see the table below for the client connection-related hooks supported:
| Name | Required or Not | Description | Supported Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|
client.connect | Optional | Number of client connection requests, including successful or failed connection requests | All gateways |
client.connack | Optional | Number of CONNACK messages received by the clients | All gateways |
client.authenticate | Required | Number of clients authenticated | |
client.connected | Required | Number of clients connected successfully | All gateways |
client.disconnected | Required | Number of clients disconnected, including active or abnormal disconnections | All gateways |
client.authorize | Required | Number of authorized clients publish/subscribe requests | All gateways |
client.subscribe | Optional | Number of client's attempts to subscribe to a topic | MQTT-SN STOMP |
client.unsubscribe | Optional | Number of client's attempts to unsubscribe from a topic | MQTT-SN STOMP |
Session and message-related hooks have no heterogeneity issues between protocols, so these hooks are fully supported for each type of gateway.
For a detailed explanation of hooks, see Hooks.