STOMP Gateway
EMQX STOMP Gateway is a messaging protocol translator that bridges the gap between STOMP and MQTT protocols, allowing clients using these protocols to communicate with each other.
This STOMP Gateway provides a lightweight and simple messaging solution for clients and servers, enabling message exchange in a variety of messaging environments. With its support for TCP and SSL-type listeners, the STOMP gateway is a flexible and versatile tool for building messaging systems.
TIP
The STOMP gateway is based on Stomp v1.2 and is compatible with STOMP v1.0 and v1.1 specifications.
Enable STOMP Gateway
In EMQX 5.0, STOMP gateway can be configured and enabled through the Dashboard, HTTP API, and configuration file emqx.conf. This section takes the configuration via Dashboard as an example to illustrate the operating steps.
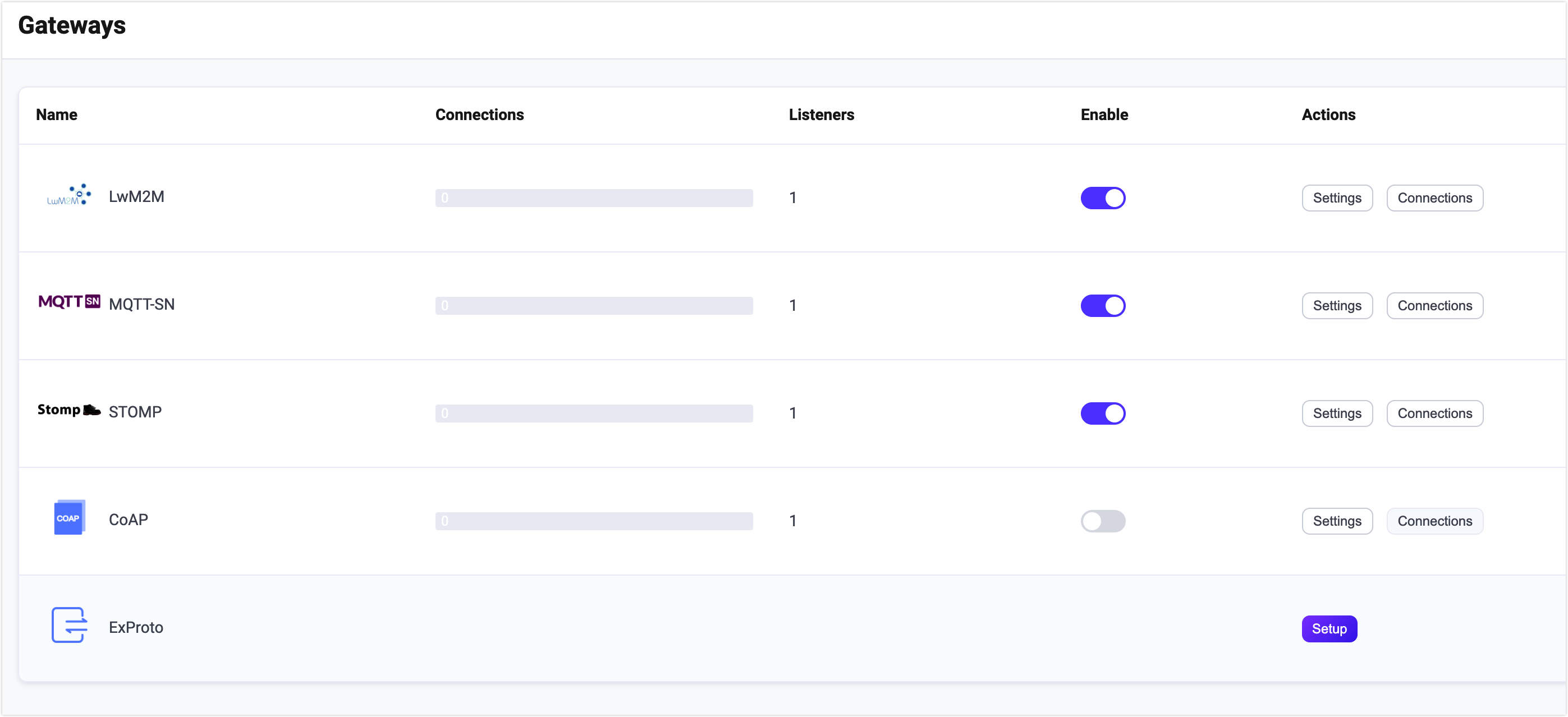
On EMQX Dashboard, click Management -> Gateways on the left navigation menu. On the Gateways page, all supported gateways are listed. Locate STOMP and click Setup in the Actions column. Then, you will be directed to the Initialize STOMP page.
TIP
If you are running EMQX in a cluster, the settings you made through the Dashboard or HTTP API will affect the whole cluster. If you only want to change the settings with one node, configure with emqx.conf.
To simplify the configuration process, EMQX offers default values for all required fields on the Gateways page. If you don't need extensive customization, you can enable the STOMP Gateway in just 3 clicks:
- Click Next in the Basic Configuration tab to accept all the default settings.
- Then you will be directed to the Listeners tab, where EMQX has pre-configured a UDP listener on port
61613. Click Next again to confirm the setting. - Then click the Enable button to activate the STOMP Gateway.
Upon completing the gateway activation process, you can return to the Gateways page and observe that the STOMP Gateway now displays an Enabled status.
In EMQX 5.0, Stomp gateways can be configured and enabled through the Dashboard.
The above configuration can also be configured with HTTP API:
Example Code:
curl -X 'PUT' 'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateways/stomp' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"name": "stomp",
"enable": true,
"mountpoint": "stomp/",
"listeners": [
{
"type": "tcp",
"name": "default",
"bind": "61613",
"max_conn_rate": 1000,
"max_connections": 1024000
}
]
}'Work with STOMP Clients
Client Libraries
After establishing the STOMP gateway, you can use the STOMP client tools to test the connections and ensure everything works as expected. Below are some of the recommended STOMP client tools.
Publish/Subscribe
The STOMP protocol is fully compatible with the PUB/SUB messaging model, and the STOMP gateway uses:
- The
SENDmessage of the STOMP protocol for message publishing. Thedestinationfield in theSENDmessage specifies the topic, while the message content is contained in the body of theSENDmessage. The quality of service (QoS) is fixed at 0. - The
SUBSCRIBEmessage of the STOMP protocol for subscribing requests. Thedestinationfield in theSUBSCRIBEmessage specifies the topic. The QoS is fixed at 0 and the wildcards defined in the MQTT protocol are supported. - The
UNSUBSCRIBEmessage of the STOMP protocol for unsubscribing requests. Thedestinationfield in theSUBSCRIBEmessage specifies the topic.
Customize Your STOMP Gateway
In addition to the default settings, EMQX provides a variety of configuration options to better accommodate your specific business requirements. This section offers an in-depth overview of the various fields available on the Gateways page.
Basic Configuration
In the Basic Configuration tab, you can set the maximum header allowed, the header length allowed, and whether to enable statistics or set the MountPoint string for this gateway. See the texts below the screenshot for a comprehensive explanation of each field.
Max Header: Set the maximum allowed number of STOMP Header, default:
10.Max Each Header Length: Set the maximum allowed string length of the Header value, default:
1024.Max Body Length: Set the maximum allowed bytes of the STOMP packet, default:
65536.Idle Timeout: Set the maximum amount of time in seconds that the gateway will wait for a STOMP frame before closing the connection due to inactivity.
Enable Statistics: Set whether to allow the Gateway to collect and report statistics; default:
true, optional values:true,false.MountPoint: Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols, for example, stomp/.
Note: This topic prefix is managed by the gateway. Clients do not need to add this prefix explicitly when publishing and subscribing.
Add Listeners
One tcp listener with the name of default is already configured on port 61613, which allows a maximum of 16 acceptors in the pool, and support up to 1,024,000 concurrent connections. You can click Settings for more customized settings, click Delete to delete the listener, or click + Add Listener to add a new listener.
TIP
The Stomp gateway only supports TCP and SSL types of listeners.
Click Add Listener to open Add Listener page, where you can continue with the following configuration fields:
Basic settings
- Name: Set a unique identifier for the listener.
- Type: Select the protocol type, for STOMP, this can be either tcp or ssl.
- Bind: Set the port number on which the listener accepts incoming connections.
- MountPoint (optional): Set a string that is prefixed to all topics when publishing or subscribing, providing a way to implement message routing isolation between different protocols.
Listener Settings
- Acceptor: Set the size of the acceptor pool, default 16.
- Max Connections: Set the maximum number of concurrent connections that the listener can handle, default: 1024000.
- Max Connection Rate: Set the maximum rate of new connections the listener can accept per second, default: 1000.
- Proxy Protocol: Set to enable protocol V1/2 if EMQX is configured behind the load balancer.
- Proxy Protocol Timeout: Set the maximum amount of time in seconds that the gateway will wait for the proxy protocol package before closing the connection due to inactivity, default: 3s.
TCP Settings
- ActiveN: Set the
{active, N}option for the socket, that is, the number of incoming packets the socket can actively process. For details, see Erlang Documentation - setopts/2. - Buffer: Set the size of the buffer used to store incoming and outgoing packets, unit: KB.
- TCP_NODELAY: Set whether to enable the
TCP_NODELAYflat for the connection, that is, whether the client needs to wait for the acknowledgment of the previous data before sending additional data; default: false, optional values: true, false. - SO_REUSEADDR: Set whether to allow local reuse of port numbers.
- Send Timeout: Set the maximum amount of time in seconds that the gateway will wait for the proxy protocol package before closing the connection due to inactivity, default: 15s.
- Send Timeout: Set whether to close the connection if the send timeout.
**SSL Settings **(for SSL listeners only)
You can set whether to enable the TLS Verify by setting the toggle switch. But before that, you need to configure the related TLS Cert, TLS Key, and CA Cert information, either by entering the content of the file or uploading with the Select File button. For details, see Enable SSL/TLS Connection.
Then you can continue to set:
- SSL Versions: Set the SSL versions supported, default, tlsv1.3 tlsv1.2, tlsv1.1, and tlsv1.
- Fail If No Peer Cert: Set whether EMQX will reject the connection if the client sends an empty certificate, default: false, optional values: true, false.
- Intermediate Certificate Depth: Set the maximum number of non-self-issued intermediate certificates that can be included in a valid certification path following the peer certificate, default, 10.
- Key Password: Set the user's password, used only when the private key is password-protected.
Configure Authentication
As the concept of username and password is already defined in the connection message of the Stomp protocol, the STOMP supports a variety of authenticator types, such as:
- Built-in Database Authentication
- MySQL Authentication
- MongoDB Authentication
- PostgreSQL Authentication
- Redis Authentication
- HTTP Server Authentication
- JWT Authentication
- LDAP Authentication
Stomp gateway uses the information in the CONNECT or STOMP message of the STOMP protocol to generate the authentication fields for the client:
- Client ID: Randomly generated string
- Username: Value of the
loginfield in theCONNECTorSTOMPmessage headers - Password: Value of the
passcodefield in theCONNECTorSTOMPmessage headers.
You can also use HTTP API to create a built-in database authentication for a Stomp gateway:
Example Code:
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://127.0.0.1:18083/api/v5/gateway/stomp/authentication' \
-u <your-application-key>:<your-security-key> \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"backend": "built_in_database",
"mechanism": "password_based",
"password_hash_algorithm": {
"name": "sha256",
"salt_position": "suffix"
},
"user_id_type": "username"
}'TIP
Unlike the MQTT protocol, the gateway only supports the creation of an authenticator, not a list of authenticators (or an authentication chain).
When no authenticator is enabled, all STOMP clients are allowed to log in.